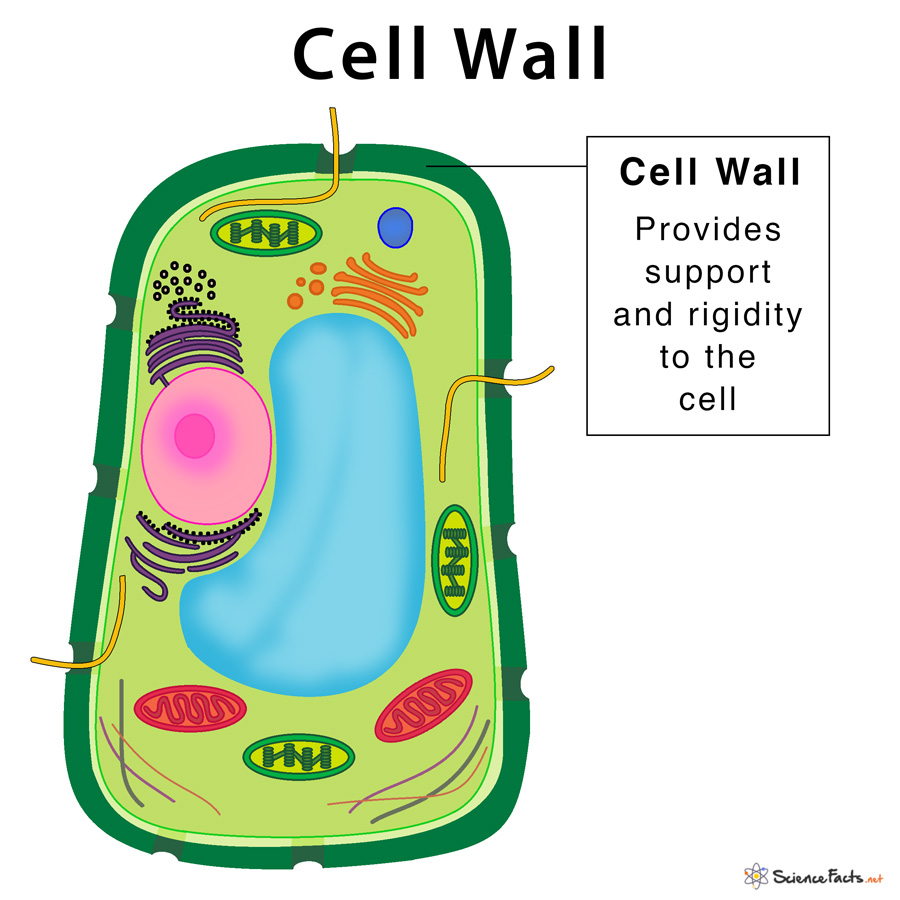
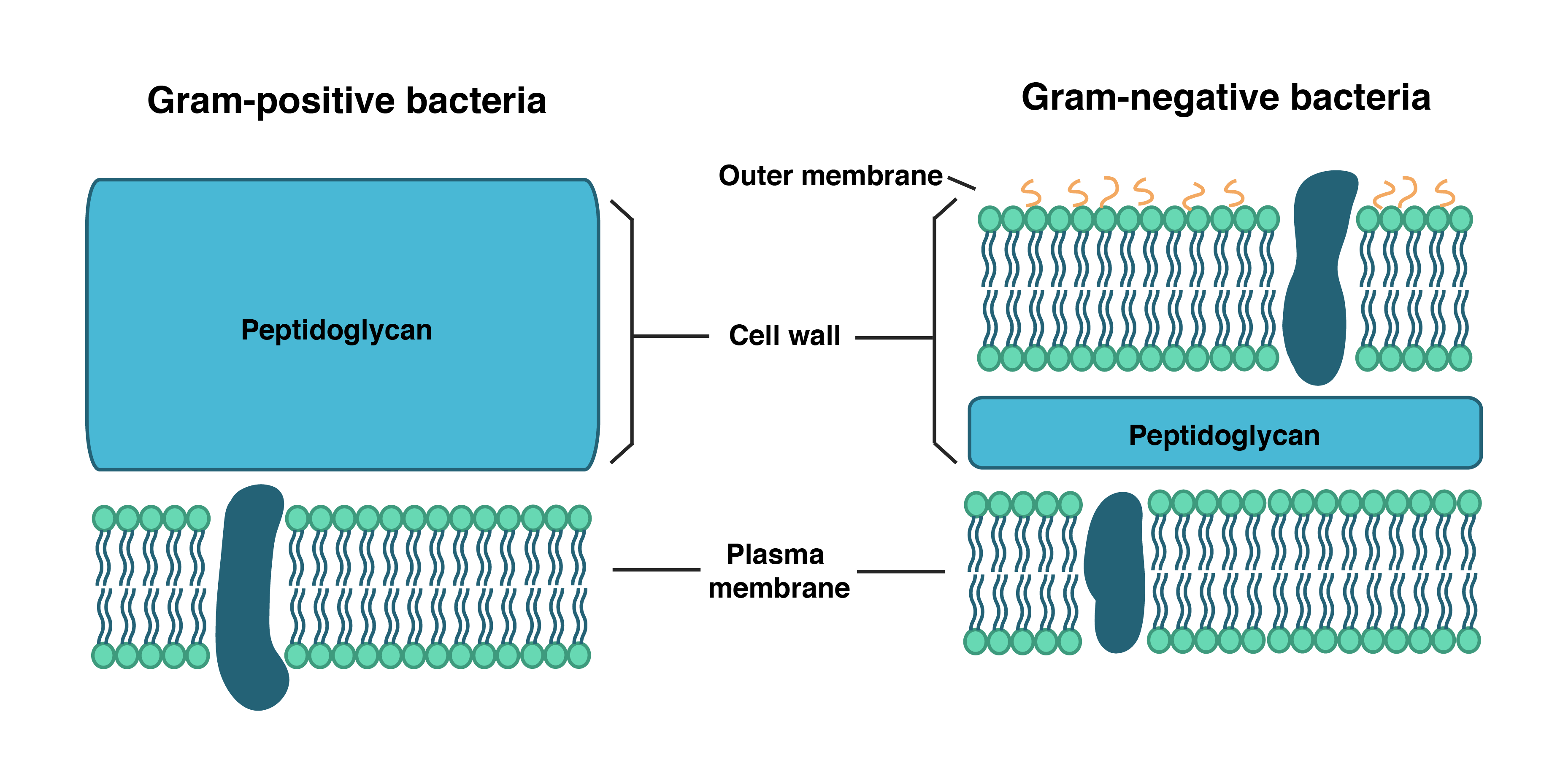
Web the main functions of the cell wall are: Unit 7 more about cells. Providing the strength, structural support and maintaining the shape of the cell. It can be tough, flexible, and sometimes rigid. Fungal and protistan cells also have cell walls, as do some prokaryotic cells.
Cells contain parts called organelles. Unit 8 membranes and transport. Web an animal cell lacks a cell wall or chloroplasts. Its facts, meaning, analogy, composition, description, location, & purpose with examples, & labeled picture. Unit 2 water, acids, and bases.
The cell wall distinguishes plant cells from animal cells and provides physical support and protection. Cells contain parts called organelles. Cells must be able to exclude, take in, and excrete various substances, all in specific amounts. It is the outer rigid protective supportive and semi transparent covering of plant cells, fungi and some protists. Its facts, meaning, analogy, composition, description, location, & purpose with examples, & labeled picture.
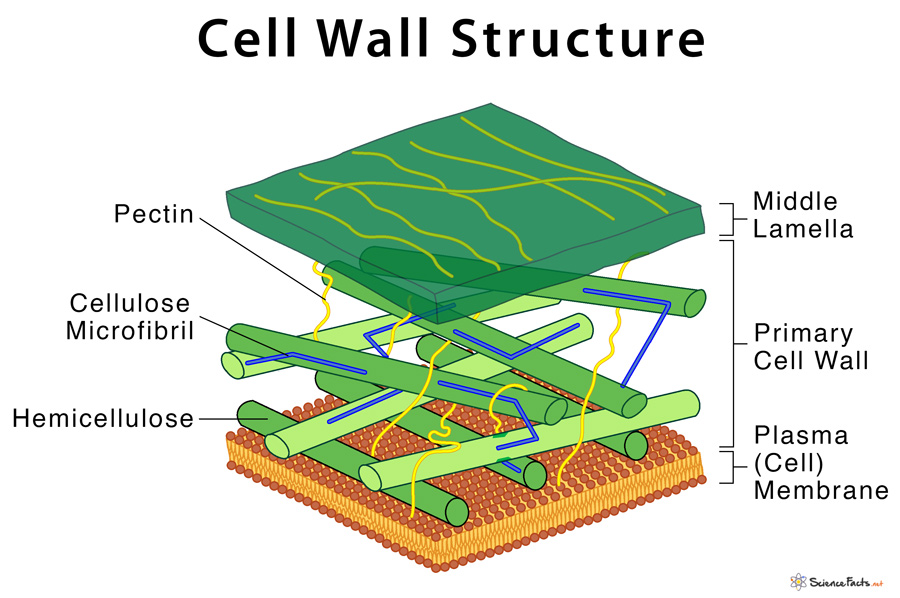
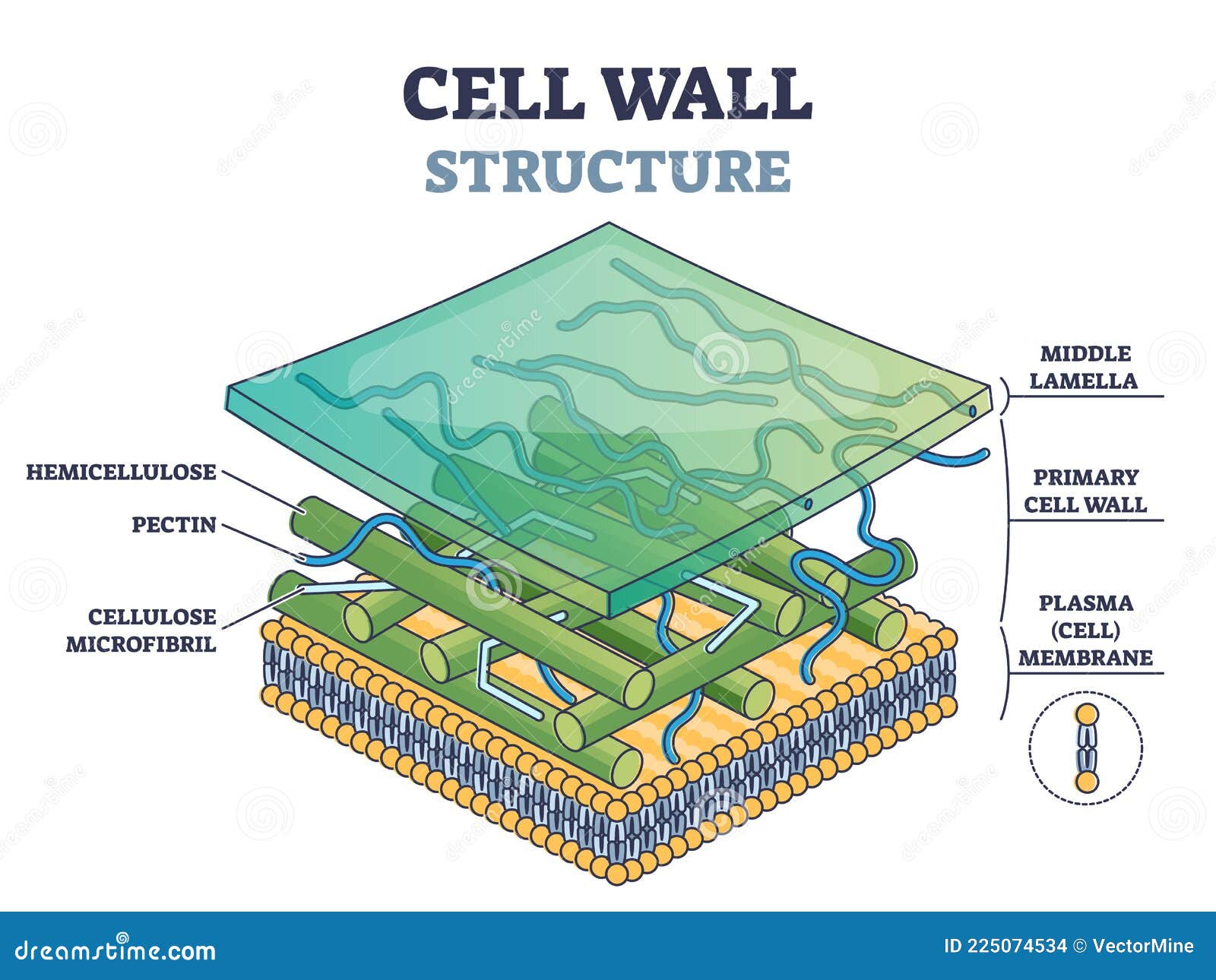
Cell structures and their functions. Web meaning of cell wall: It is primarily made up of carbohydrates like pectin, cellulose and hemicellulose. Web plants and fungi have a tough cell wall for protection and support, while animal cells can secrete materials into their surroundings to form a meshwork of macromolecules called the extracellular matrix. Web the cell wall is a rigid covering that protects the cell, provides structural support, and gives shape to the cell. Web the cell wall is a rigid covering that protects the cell, provides structural support, and gives shape to the cell. A cell wall is an outer layer surrounding certain cells that is outside of the cell membrane. Cells contain parts called organelles. In figure \(\pageindex{1}\), the diagram of a plant cell, you see a structure external to the plasma membrane which is the cell wall. Web unit 1 intro to biology. Unit 4 elements of life. It is present around the plasma membrane. Unit 2 water, acids, and bases. Web the cell wall surrounds the plant cell, providing both structure and protection. Providing the strength, structural support and maintaining the shape of the cell.
Unit 2 Water, Acids, And Bases.
Unit 8 membranes and transport. Start practicing—and saving your progress—now: Web unit 1 intro to biology. Web plants and fungi have a tough cell wall for protection and support, while animal cells can secrete materials into their surroundings to form a meshwork of macromolecules called the extracellular matrix.
Unit 6 Structure Of A Cell.
In figure \(\pageindex{1}\), the diagram of a plant cell, you see a structure external to the plasma membrane which is the cell wall. It is the outer rigid protective supportive and semi transparent covering of plant cells, fungi and some protists. Primarily, it provides the cell with structural support, shape, protection, and functions as a selective barrier. The cell wall distinguishes plant cells from animal cells and provides physical support and protection.
Animal Cells However, Do Not Have A.
Web cell wall, specialized form of extracellular matrix that surrounds every cell of a plant. It is present around the plasma membrane. Web the cell wall separates the interior contents of the cell from the exterior environment. It is primarily made up of carbohydrates like pectin, cellulose and hemicellulose.
Its Facts, Meaning, Analogy, Composition, Description, Location, & Purpose With Examples, & Labeled Picture.
Web courses on khan academy are always 100% free. Its outer coating is a semipermeable cell membrane. Web the primary cell wall is the first wall formed by the cell that gets deposited on either side of the middle lamella of the adjacent cells. Fungal and protistan cells also have cell walls, as do some prokaryotic cells.



:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Plant_cell_wall_diagram-en.svg-58a8766c3df78c345bdc5df3.png)