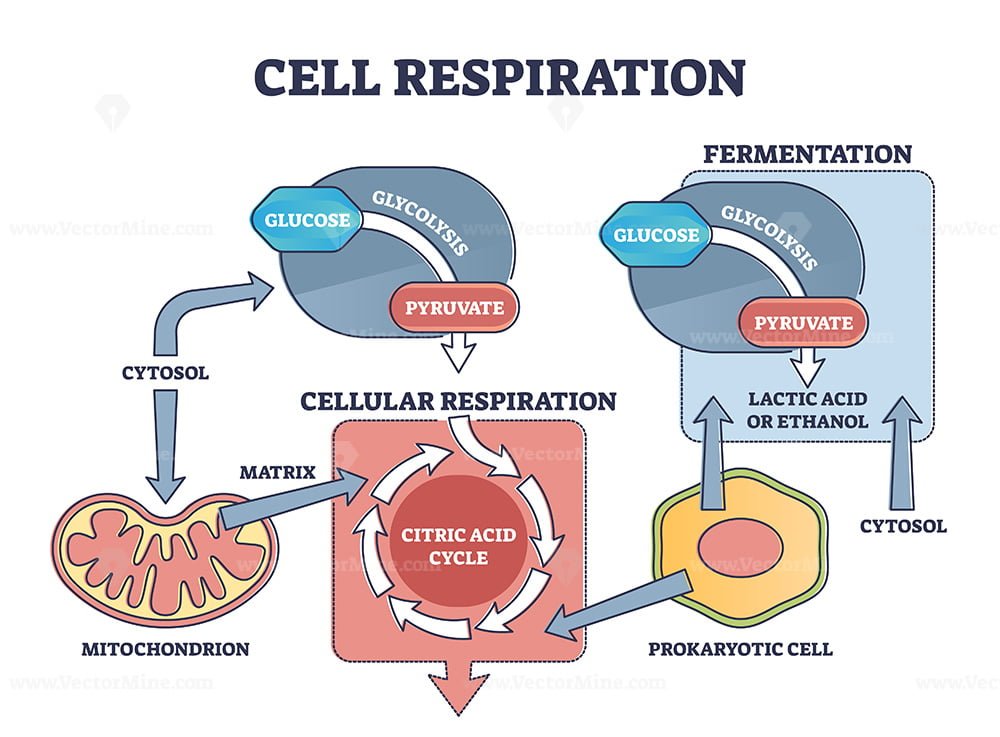
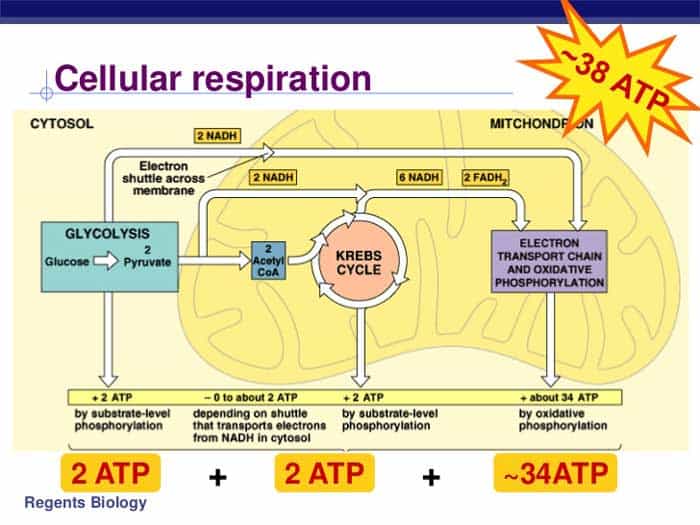
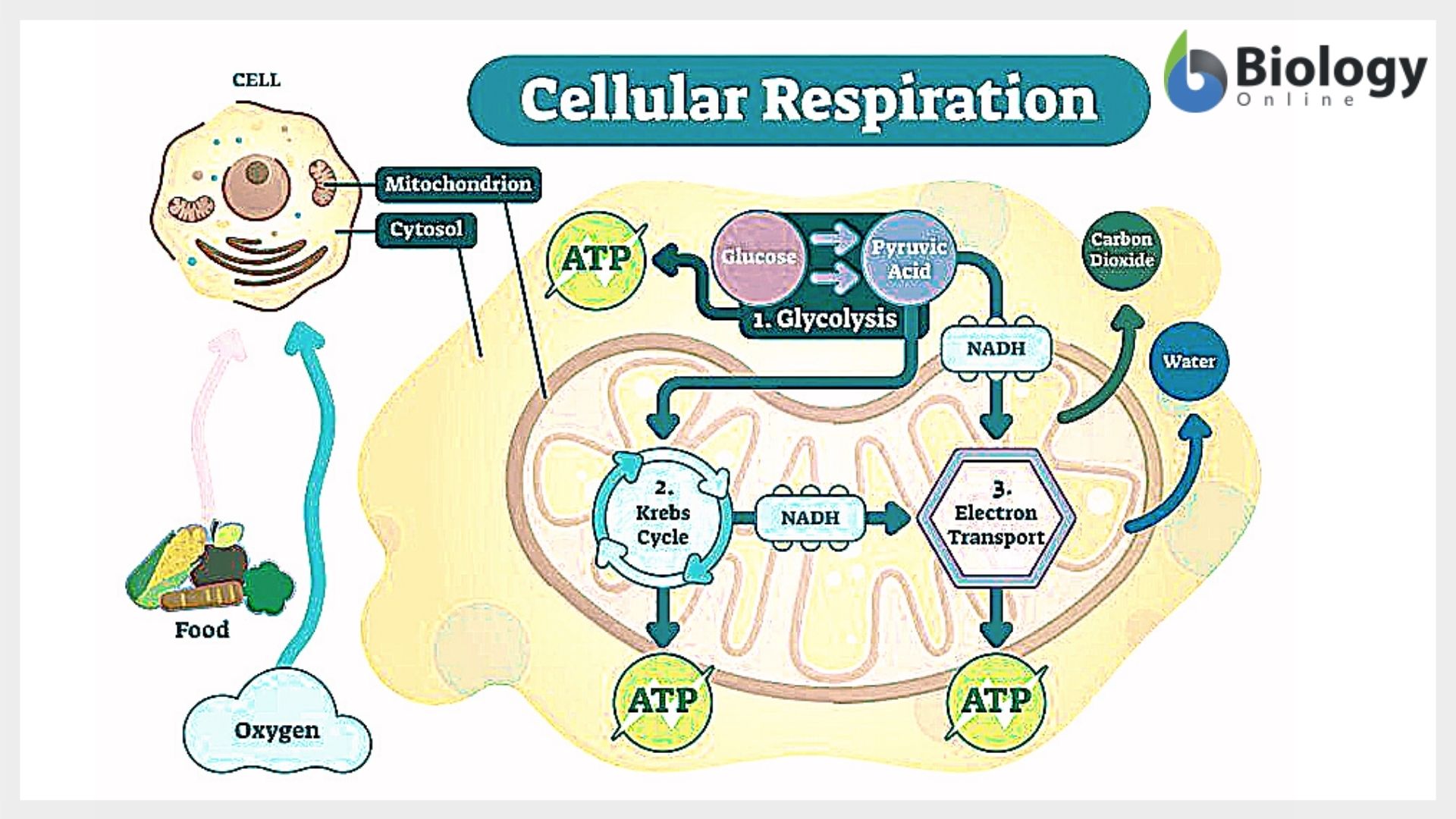
The chemical reaction for cellular respiration involves glucose and oxygen as inputs, and produces carbon dioxide, water, and energy (atp) as outputs. The stages of cellular respiration include glycolysis, pyruvate oxidation, the citric acid or krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. Unit 6 structure of a cell. Explore cellular respiration equation, types, stages & products via diagrams. In multicellular organisms, the steps of cellular respiration occur in the cytosol and the mitochondria.
Explore cellular respiration equation, types, stages & products via diagrams. Add to the figure below to describe as much as you can about the processes that contribute to making atp. Web cellular respiration is the process by which cells derive energy from glucose. State what happens during glycolysis. This can be seen in the overall equation for cellular respiration:
Web cellular respiration is the process by which cells derive energy from glucose. Web cellular respiration is the process of which biological fuels are oxidised in the presence of an inorganic electron acceptor such as oxygen to produce large amounts of energy, to drive the bulk production of atp. Glycolysis happens in the cytosol and breaks glucose into two pyruvate, producing 2 atps and 2 nadhs. Outline the steps of the krebs cycle. The inner and outer membranes of the mitochondrion play an important roles in aerobic respiration.
This can be seen in the overall equation for cellular respiration: Web glucose and oxygen are inputs of cellular respiration. Web cellular respiration is a metabolic pathway that breaks down glucose and produces atp. Web cellular respiration (a three stage process) converts glucose and oxygen to atp (the cellular form of energy) and releases carbon dioxide and water. Carbon dioxide and water are outputs. Web cellular respiration is a metabolic pathway that uses glucose to produce adenosine triphosphate (atp), an organic compound the body can use for energy. Web cellular respiration is the process through which cells convert sugars into energy. Describe the structure of a mitochondrion. Cellular respiration has three stages: Web understand cellular respiration and cellular respiration steps. Glycolysis happens in the cytosol and breaks glucose into two pyruvate, producing 2 atps and 2 nadhs. Web cellular respiration is the process by which living organisms produce energy. In multicellular organisms, the steps of cellular respiration occur in the cytosol and the mitochondria. Web cellular respiration takes the energy stored in glucose and transfers it to atp. Web glycolysis converts glucose from the food we eat into molecules that enter downstream cellular respiration processes.
Web How To Draw Cellular Respiration Diagram In Easy Way.
Learn how to draw the cellular respiration diagram and write the equation for cellular respiration. Web students complete a graphic organizer that shows the process of cellular respiration. Web what is the purpose of cellular respiration? Web glucose and oxygen are inputs of cellular respiration.
Web Cellular Respiration Is A Metabolic Pathway That Breaks Down Glucose And Produces Atp.
Describe the structure of a mitochondrion. Unit 4 elements of life. The process has three main parts: Web understand cellular respiration and cellular respiration steps.
Web Glycolysis Converts Glucose From The Food We Eat Into Molecules That Enter Downstream Cellular Respiration Processes.
Glycolysis happens in the cytosol and breaks glucose into two pyruvate, producing 2 atps and 2 nadhs. Provide a concise summary of the process. Cellular respiration is a series of metabolic processes that take place within a cell in which the biochemical energy is harvested from an organic substance (e.g. In multicellular organisms, the steps of cellular respiration occur in the cytosol and the mitochondria.
The Stages Of Cellular Respiration Include Glycolysis, Pyruvate Oxidation, The Citric Acid Or Krebs Cycle, And Oxidative Phosphorylation.
Web cellular respiration is a process that takes place within the cells of organisms where energy is released by breaking down the chemical bonds of glucose (c 6 h 12 o 6). Add to the figure below to describe as much as you can about the processes that contribute to making atp. Web unit 1 intro to biology. Unit 6 structure of a cell.



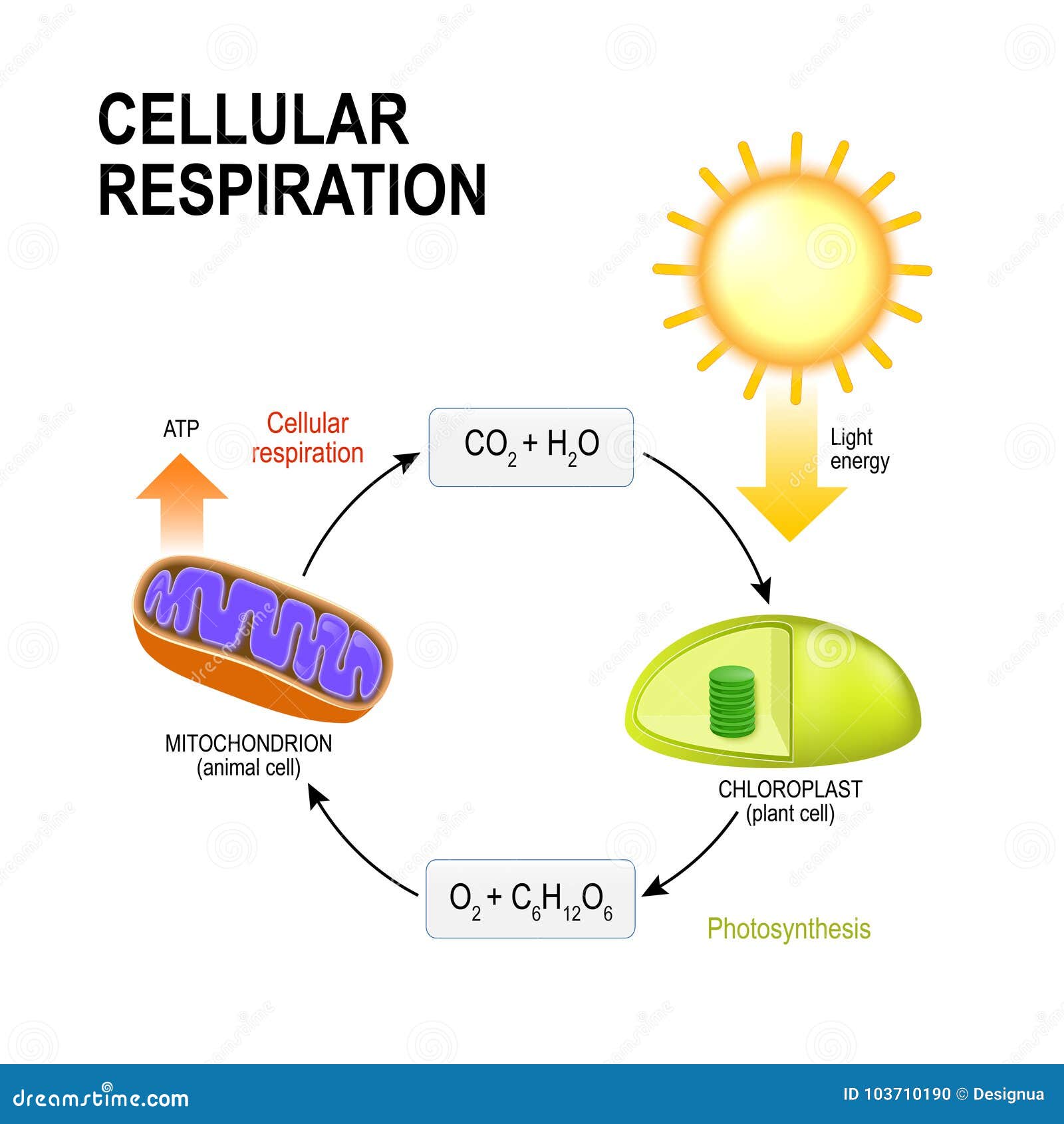

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/cellular_respiration-8fcc3f1ad3e54a828dabc02146ce4307.jpg)