The electron configuration for zn +2: H #1s^1# he #1s^2# li #1s^2 2s^1# be #1s^2 2s^2# b #1s^2 2s^2 2p^1# c #1s^2 2s^2 2p^2# n #1s^2 2s^2 2p^3# o #1s^2. As mentioned above, the electron configuration of zinc is 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 4s 2 3d 10. Just replace this portion of zinc's electron notation with argon's chemical symbol in brackets ([ar].) so, zinc's electron configuration written in shorthand is [ar]4s 2 3d 10. Two electrons can go into the 1s subshell, 2 can go into the 2s subshell, and 6 can go into the 2p subshell.
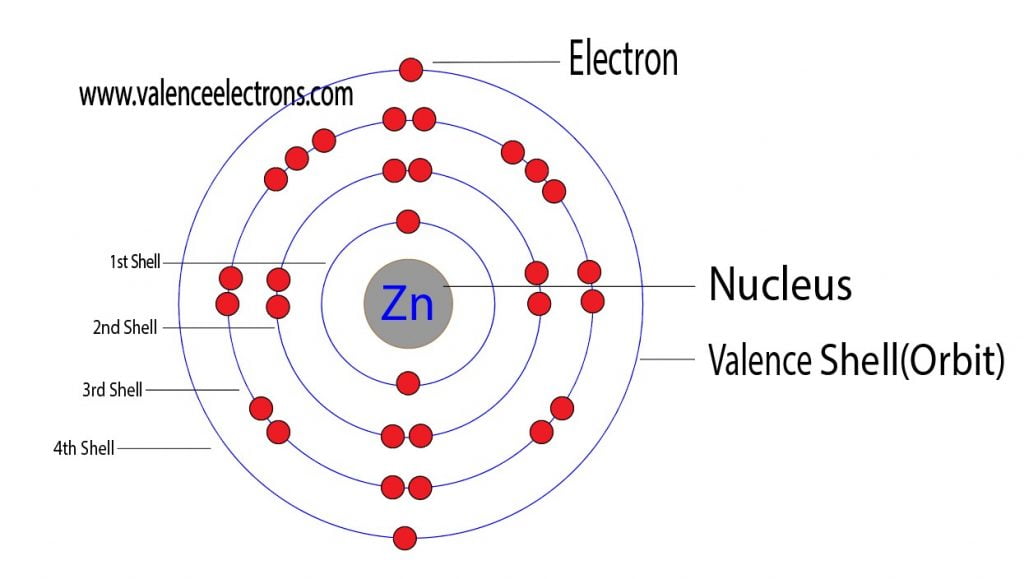
_30^65zn the zinc atom has 30 protons => 30 electrons. Web the arrangement of electrons in the orbitals of an atom is called the electron configuration of the atom. Write the electron configuration for the neutral atom and then determine the number of electrons that are lost to form the cation. The electron configuration shows that the last shell of zinc has two. Web to write the configuration for the zinc and the zinc ion, first we need to write the electron configuration for just zinc (zn).
Web now in the next step, start drawing the orbital diagram for zinc. Before drawing the orbital diagram, you should know the three general rules. Web a neutral helium atom, with an atomic number of 2. The transition metals still do not end up being isoelectronic with a. A neutral chlorine atom has 17 electrons.
Ground state zinc orbital diagram. Web therefore, the number of protons is equal to the number of electrons. These two electrons right here in the 4s orbital. The electron configuration for calcium two plus would be the same as the electron configuration for the noble gas argon here. We first need to find the nu. Web an atom's ground state electron configuration describes how the electrons have distributed among the orbital shells and subshells. Before drawing the orbital diagram, you should know the three general rules. The abbreviated electron configuration of zinc is [ar] 3d 10 4s 2. We describe an electron configuration with a symbol that contains three pieces of information ( figure \(\pageindex{2}\)): The electron configuration shows that the last shell of zinc has two. The number of the principal quantum shell, n, the letter that designates the orbital type (the subshell, l), and Web using figure \(\pageindex{2}\) as your guide, write the electron configuration of a neutral chlorine atom. As mentioned above, the electron configuration of zinc is 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 4s 2 3d 10. The electron configuration of a neutral zinc atom is #1s^22s^22p^63s^23p^63d^104s^2#. When writing an electron configuration, you have to write serially.
Web Electron Configurations Are An Organized Means Of Documenting The Placement Of Electrons Based Upon The Energy Levels And Orbitals Groupings Of The Periodic Table.
1s^2, 2s^2, 2p^6, 3s^2, 3p^6, 4s^2, 3d^10. The atomic number of cl is 17. A neutral chlorine atom has 17 electrons. Two electrons can go into the 1s subshell, 2 can go into the 2s subshell, and 6 can go into the 2p subshell.
The Electron Configuration For Calcium Two Plus Would Be The Same As The Electron Configuration For The Noble Gas Argon Here.
Web therefore, the number of electrons in neutral atom of zinc is 30. Web electron configuration chart of all elements is mentioned in the table below.the shorthand electron configuration (or noble gas configuration) as well as full. The electronic configuration of zinc in the ground state is 1 s 2 2 s 2 2 p 6 3 s. Web using figure \(\pageindex{2}\) as your guide, write the electron configuration of a neutral chlorine atom.
Its Atomic Number Is 30, So Its Complete Electron Configuration Is 1S2 2S22P6 3S23P63D10 4S2.
The ground state electron configuration of zn is [ar] 3d 10 4s 2.the orbital diagram is drawn below, which. The fact that the electron configuration shows that all sublevels are full, indicates that there are no unpaired electrons. 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 3d 10 4s 2: The electron configuration for zn +2:
Web Electron Configuration Of Zinc.
The electron configuration for the first 10 elements. The two electrons that we would lose to form the calcium two plus ion are these. This indicates that zinc has the same electronic structure as the noble gas argon (ar), followed by two electrons in the 4s orbital and ten electrons in the 3d orbital. Zinc has an electron configuration of [ar]3d 10 4s 2 and is a member of the group 12 of the periodic table.





:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Zinc-58b6020f3df78cdcd83d332a.jpg)