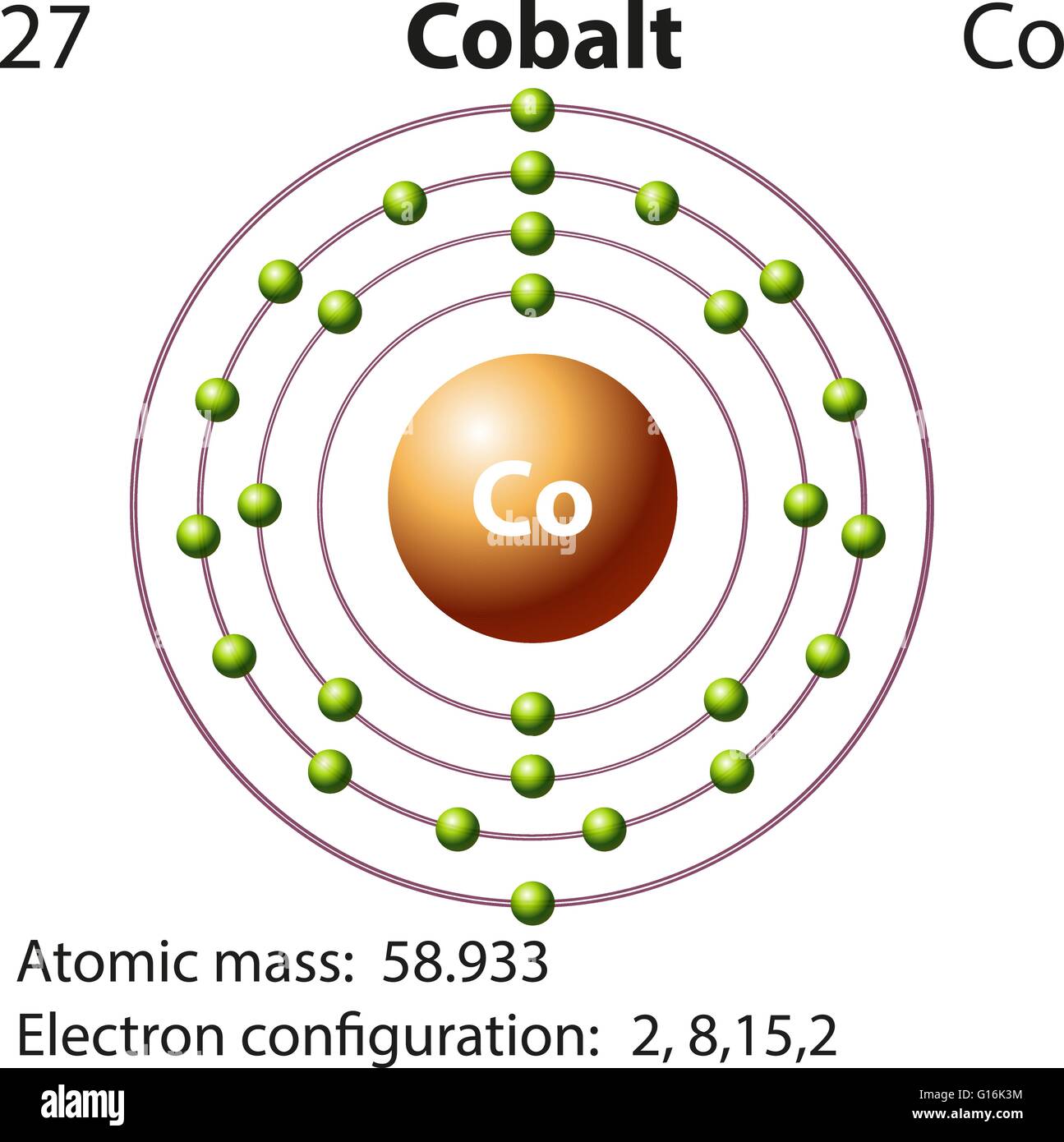
Web draw the electron configuration for a neutral atom of cobalt. 1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s² 3p⁶ 3d⁸ 4s¹. Then writing the configuration of the remaining electrons: Web to write the configuration for the cobalt ions, first we need to write the electron configuration for just cobalt (co). Web the electron configuration for a neutral cobalt atom, represented using the aufbau principle, is 1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s² 3p⁶ 4s² 3d⁷.
This represents the distribution of electrons in the atomic orbitals from lowest to highest energy levels. 1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s² 3p⁶ 3d⁸ 4s¹. 1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s² 3p⁶ 4s² 3d⁷. Web two of the three d orbitals have two electrons. Then writing the configuration of the remaining electrons:
Web to write the configuration for the cobalt ions, first we need to write the electron configuration for just cobalt (co). Determine the atomic number of cobalt from the periodic table. By knowing the electron configuration of an element, we can predict and explain a great deal of its chemistry. 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 3d 7 4s 2. 1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s² 3p⁶ 4s² 3d⁷ 4p¹.
We first need to find the number of electrons for the co atom. The atomic number of cobalt is 27, which means a neutral cobalt atom has 27 electrons. So, the more accurate electron configuration is: Web the electron configuration of a neutral atom of cobalt is 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d7. [ a r ] 3 d 7 4 s 2 \mathrm{[ar]3d^74s^2} [ ar ] 3 d 7 4 s 2 1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s² 3p⁶ 4s² 3d⁷ 4p¹. Web let us use this smart electron configuration calculator to determine the electron configuration of copper: Web to write the configuration for the cobalt ions, first we need to write the electron configuration for just cobalt (co). Web electronic structure drawing a box diagram of the electron configuration of an atom draw the electron configuration for a neutral atom of sulfur. Energy х this problem has been solved! Web the electron configuration of a neutral cobalt atom is: Draw the electron configuration for a neutral atom of cobalt. Your solution’s ready to go! Justify the anomalies of the electron configurations in transition metals using magnetism experimental data. Find the atomic number of cobalt from the periodic table.
Your Solution’s Ready To Go!
Determine the atomic number of cobalt from the periodic table. Then writing the configuration of the remaining electrons: However, to achieve a more stable configuration, one of the 4s electrons can be excited to the 3d level. Determine the number of electrons in a neutral cobalt atom.
Web The Electron Configuration Of Cobalt Is:
In this video we'll use the periodic table to help us write the notation for. Web the electron configuration of a neutral cobalt atom is: Justify the anomalies of the electron configurations in transition metals using magnetism experimental data. 1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s² 3p⁶ 4s² 3d⁷.
[ A R ] 3 D 7 4 S 2 \Mathrm{[Ar]3D^74S^2} [ Ar ] 3 D 7 4 S 2
So, the more accurate electron configuration is: Find the atomic number of cobalt from the periodic table. Justify the observed charge of ions to their electronic configuration. The atomic number of cobalt is 27, which means a neutral cobalt atom has 27 electrons.
Write The Electron Configuration For A Neutral Atom Of Manganese.
Web determine the electron configuration of ions. Check the atomic number (29) and atomic mass (63.546) of copper. In terms of energy, as you ascend from the bottom to the top of the electron configuration diagram, the energy increases. The cobalt (iii) ion, however, has lost 3.