Web bacteria are unicellular organisms with a simple structure. Describe the functions of the structures found in prokaryotic cells. In this article we will discuss about the structure of bacterial cell. Web the structure of the bacteria consists of three major parts: Diplococcus, streptococcus, tetrad, sarcina, and staphylococcus.
38k views 1 year ago #biology #science #ncert. Please don’t forget to subscribe my video. Plant, animal and bacterial cells have smaller components each with a specific function. In this case, a bacterium. Web most bacteria are, however, surrounded by a rigid cell wall made out of peptidoglycan, a polymer composed of linked carbohydrates and small proteins.
38k views 1 year ago #biology #science #ncert. Primary structure of biological macromolecules determines function. The cell envelope comprises a rigid cell wall and an underlying cytoplasmic or plasma membrane. Web prokaryotic cell diagram. By following the simple steps, you too can easily draw a perfect bacteria.
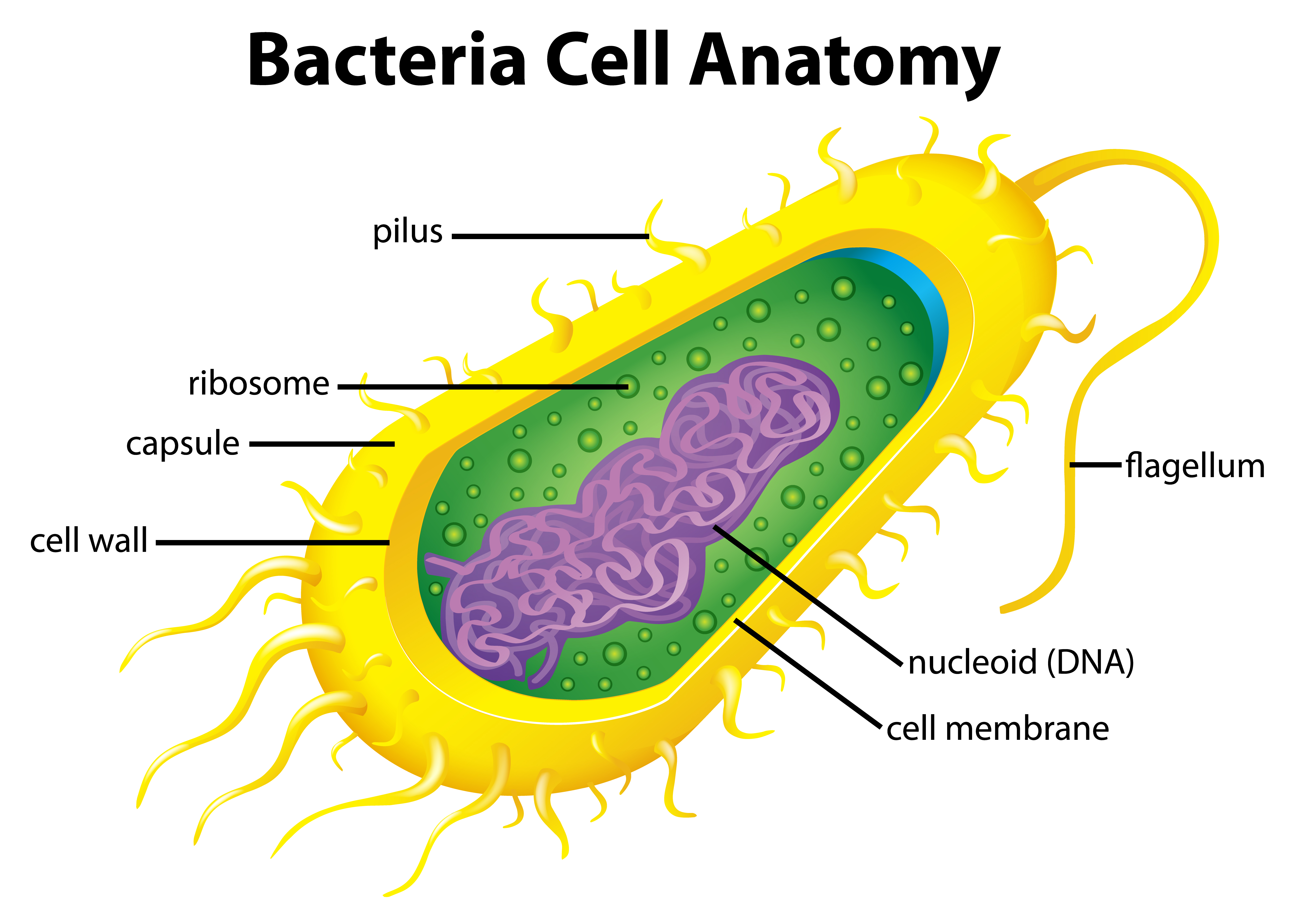
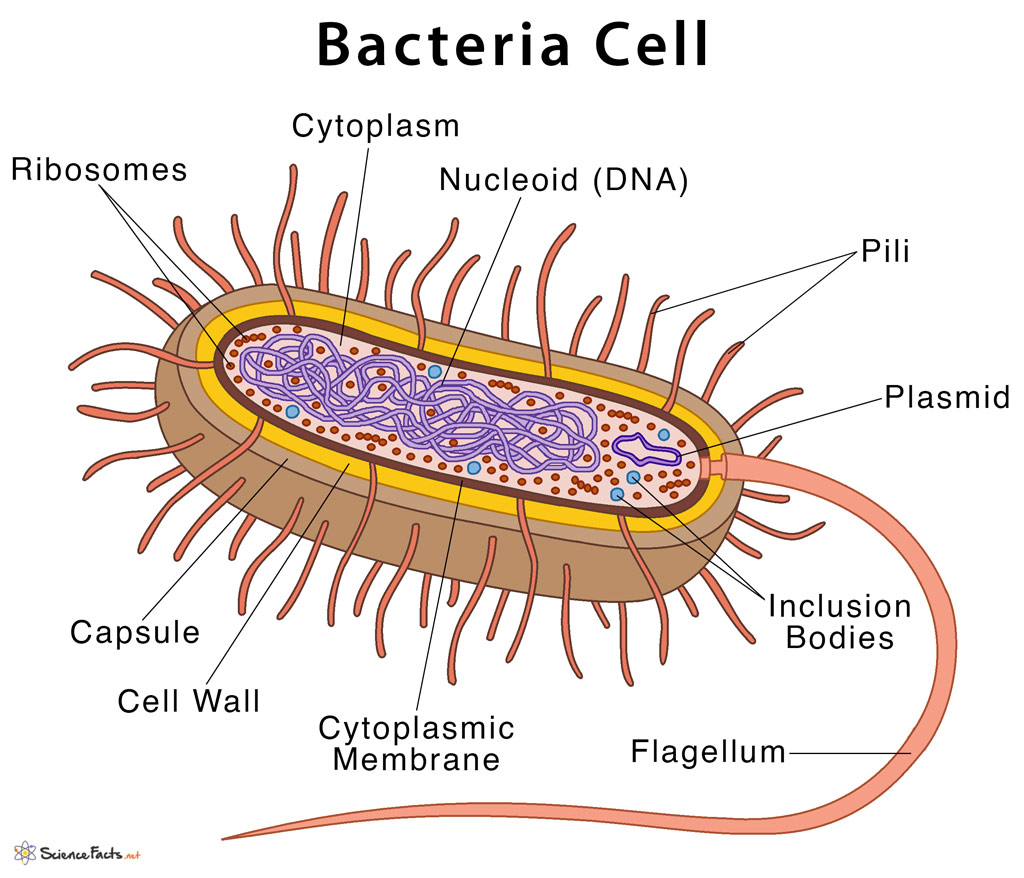
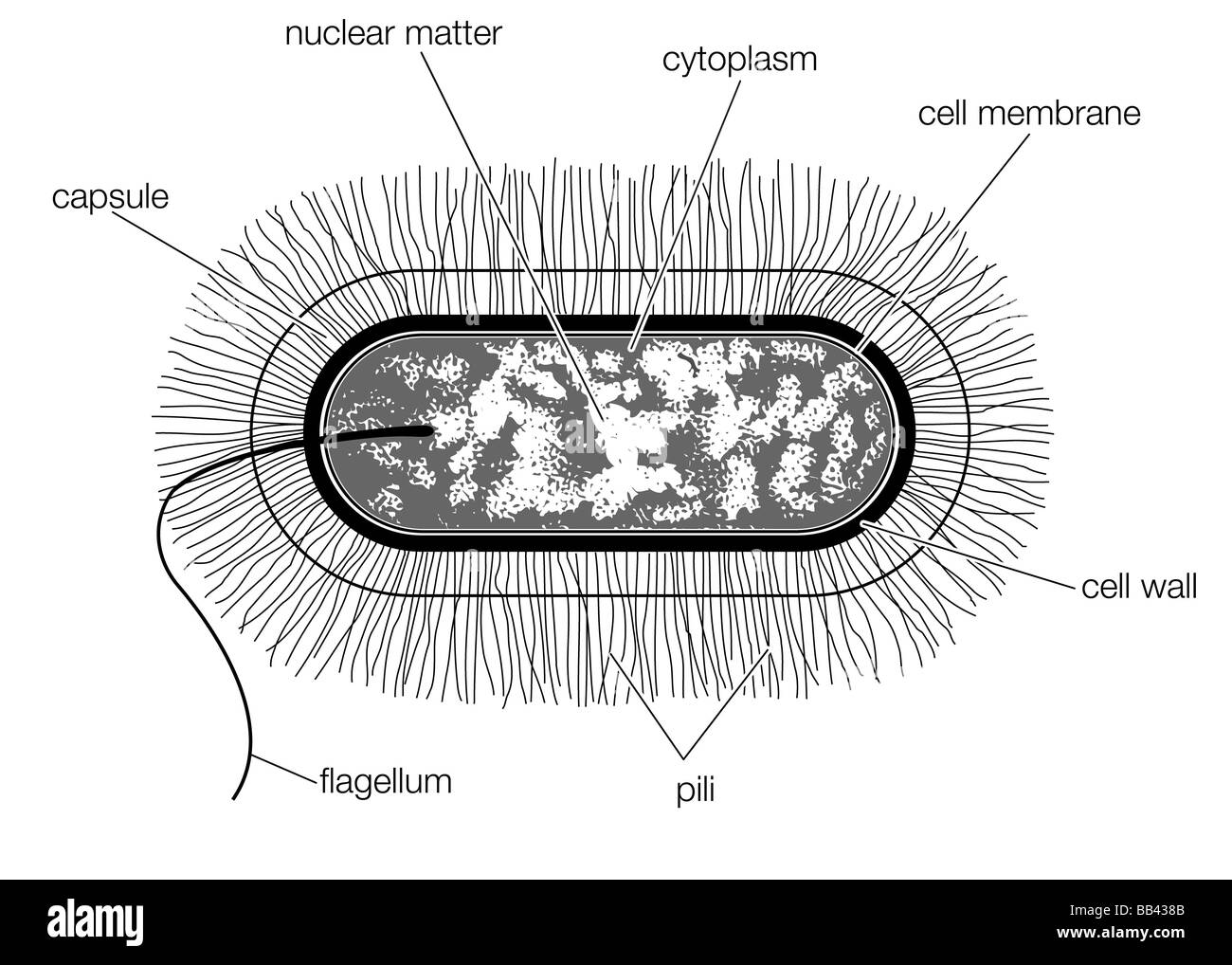
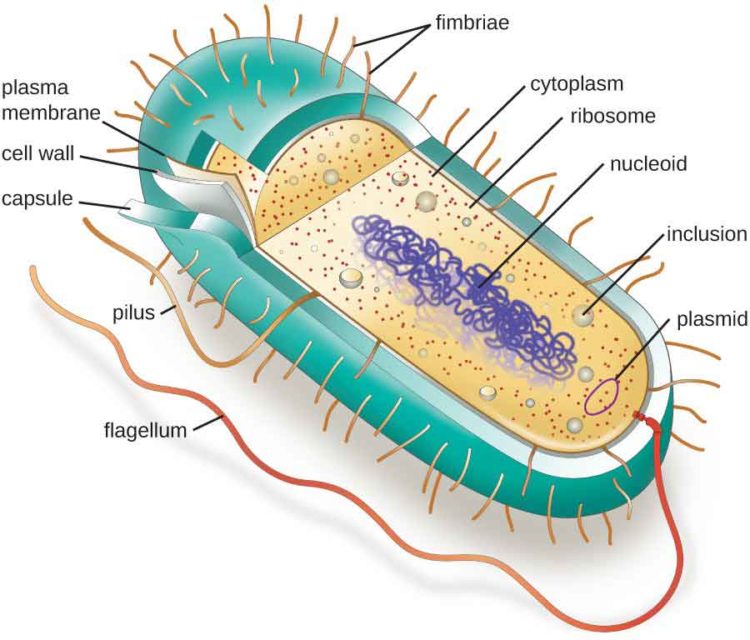
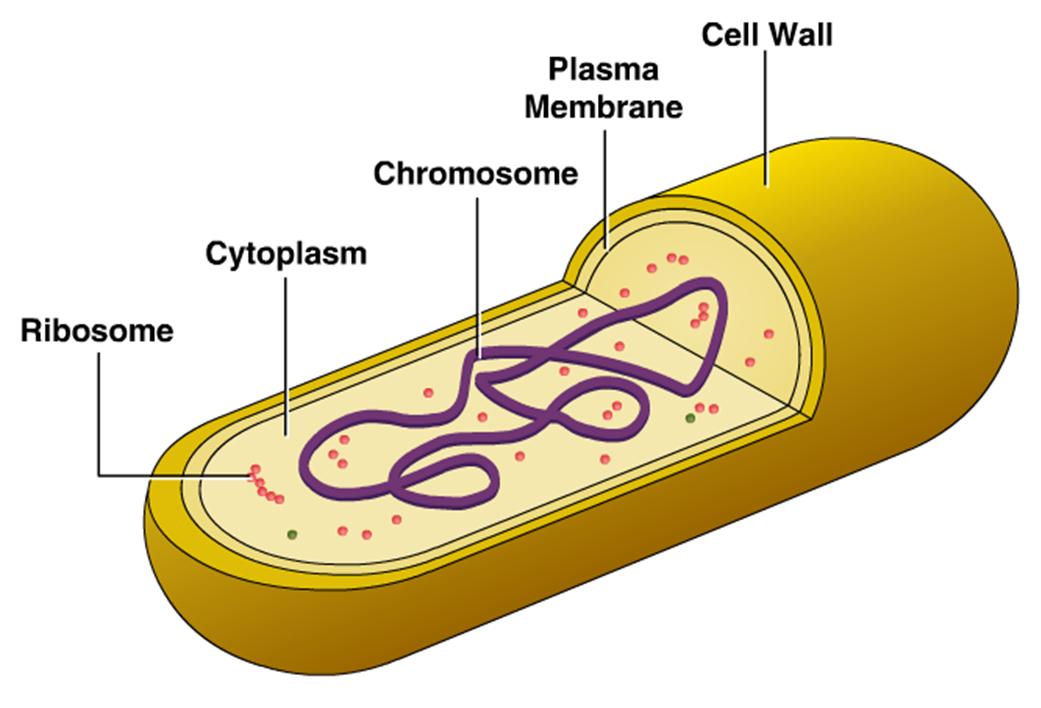
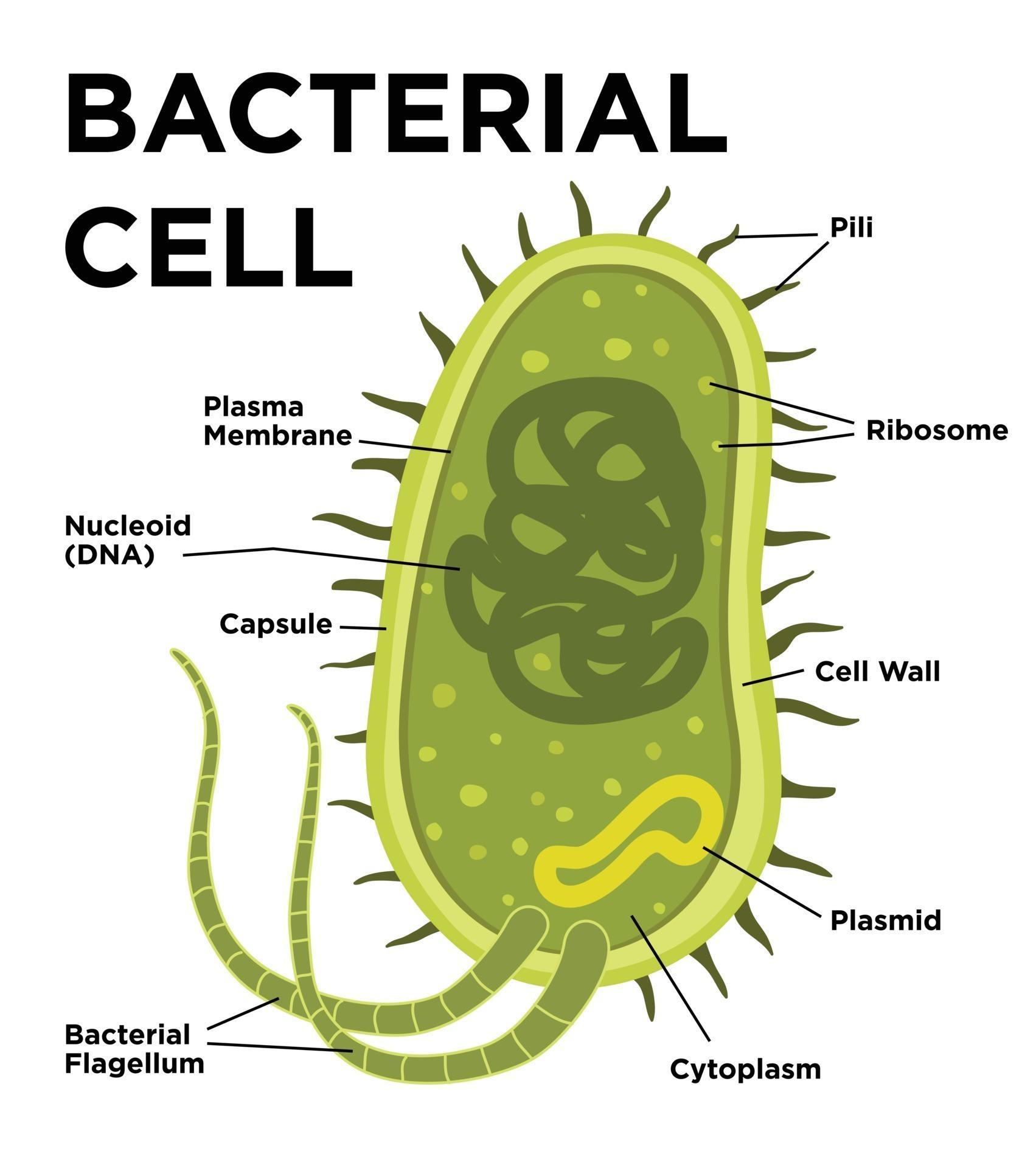
The unicell is exceedingly small in size. Web the structure of the bacteria consists of three major parts: It includes the cell wall of bacteria and the plasma membrane beneath it. The cell wall, plasmid, cytoplasm and flagella are clearly marked in the diagram. Diplococcus, streptococcus, tetrad, sarcina, and staphylococcus. In this case, a bacterium. Plant, animal and bacterial cells have smaller components each with a specific function. Web how to draw bacteria. The anatomy of a bacterial cell prokaryotic cell structure. Describe the functions of the structures found in prokaryotic cells. Bacterium) are unicellular prokaryotic microorganisms which divide by binary fission. Pilus (plural pili) plasma membrane. In this article we will discuss about the structure of bacterial cell. Web bacterial infections have long been a scourge for humanity. The following image is a diagram of a prokaryotic cell;
Primary Structure Of Biological Macromolecules Determines Function.
Procaryotic structural components consist of macromolecules such as dna, rna, proteins, polysaccharides, phospholipids, or some combination thereof. The cell wall provides an extra layer of protection, helps the cell maintain its shape, and prevents dehydration. Many structural features are unique to bacteria and. The cell envelope comprises a rigid cell wall and an underlying cytoplasmic or plasma membrane.
They Come In Many Shapes And Sizes, From Minute Spheres, Cylinders And Spiral Threads, To Flagellated Rods, And Filamentous Chains.
Little structural detail can be made out in such a small body with an ordinary light microscope. Web most bacteria are, however, surrounded by a rigid cell wall made out of peptidoglycan, a polymer composed of linked carbohydrates and small proteins. (the red dye also binds, but the violet dye covers it up.) Describe the functions of the structures found in prokaryotic cells.
Bacterium) Are Unicellular Prokaryotic Microorganisms Which Divide By Binary Fission.
Web a typical bacterial cell is structurally very similar to a plant cell. The current methods rely on the subjective reading of. There are also cell walls, cytoplasm, and nucleoids (genetic material) are present in the bacterial cell. Web the structure of the cell wall of the bacteria determines which dye is visible at the end of the procedure.
It Includes The Cell Wall Of Bacteria And The Plasma Membrane Beneath It.
The unicell is exceedingly small in size. Web geometric shape features are used to identify the morphological characteristics, namely, flagella and fimbriae or pili of bacterial cells. A typical bacterial cell resembles a plant cell and has a complex membrane, cell walls, cytoplasm, and nucleoids. Plant, animal and bacterial cells have smaller components each with a specific function.


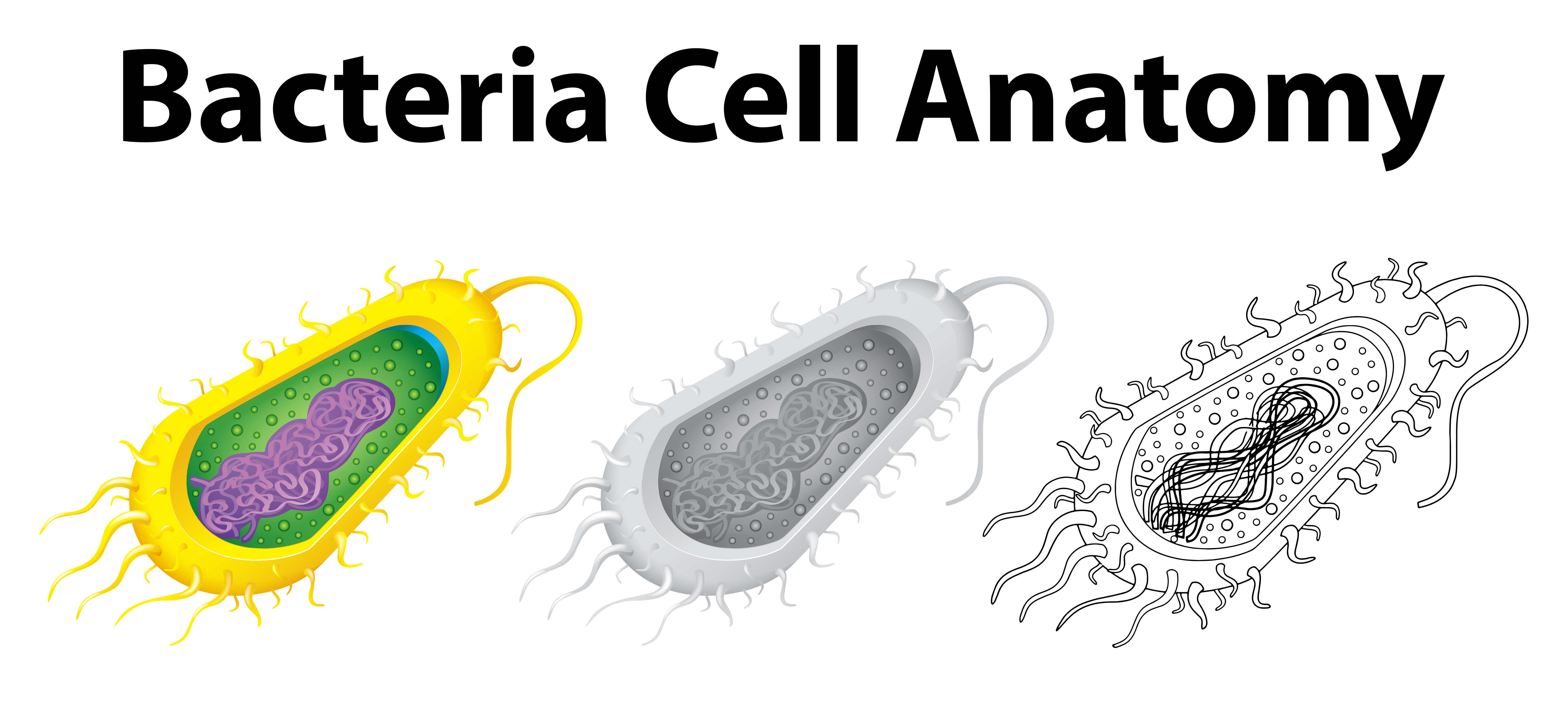
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/bacteria_cell_drawing-5786db0a5f9b5831b54f017c.jpg)